What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic Retinopathy Progresses Through Two Main Stages
Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR)
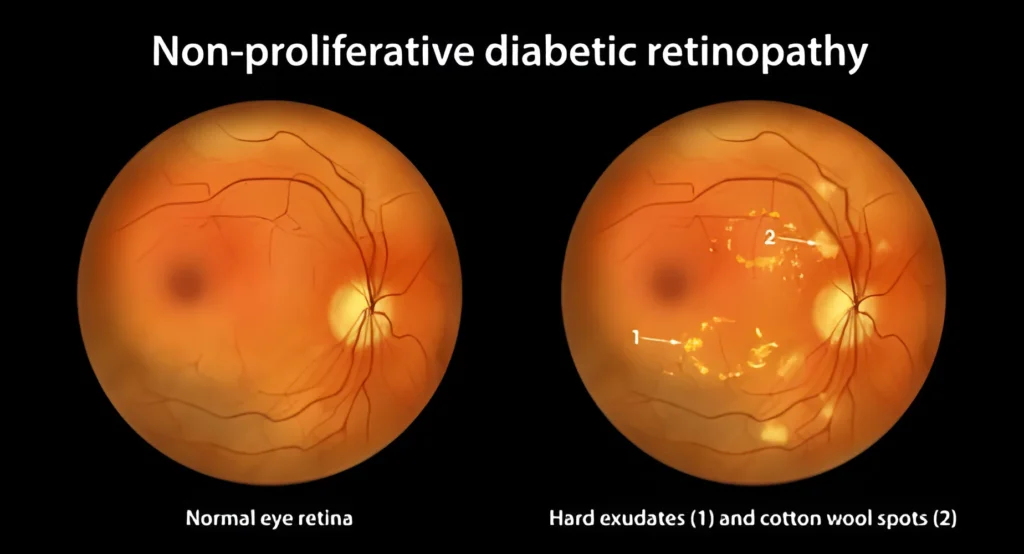
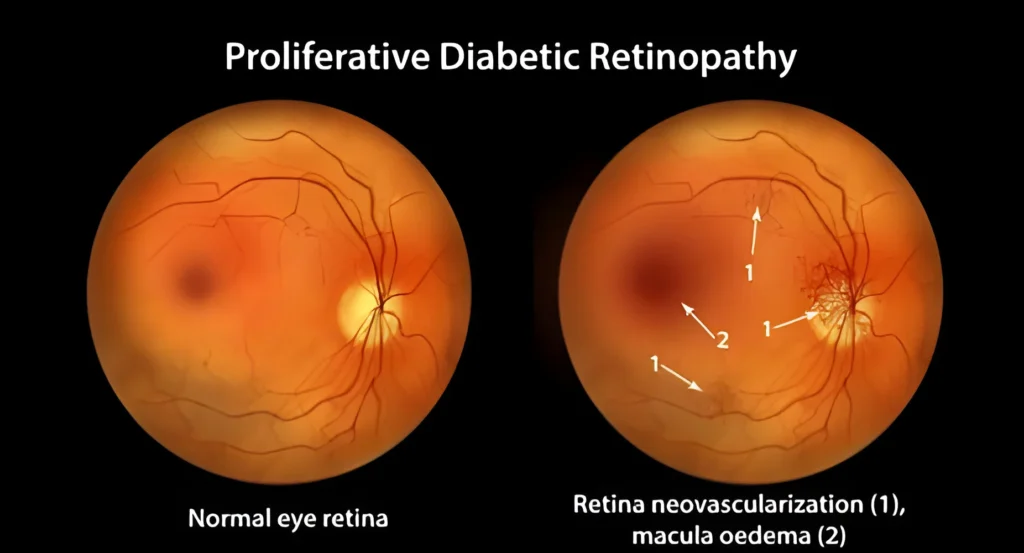
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR)
Importance of Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy
Early detection and getting the best treatment of diabetic retinopathy are crucial for preventing severe and permanent vision loss. Regular eye exams can detect retinopathy even before symptoms start to appear, allowing for the timely intervention of diabetic retina specialists. Treatments such as laser therapy, anti-VEGF injections, and vitrectomy are a few options that can slow down or halt the progression of diabetic retinopathy, preserving vision and improving quality of life.
Causes Symptoms & Diagnosis
- High Blood Sugar Levels Consistently high glucose levels are the main cause of retina blood vessel damage. Hyperglycemia can cause these vessels to become blocked, swell, or leak, leading to diabetic retinopathy. Effective blood sugar management is the first step in preventing the start and progression of diabetic retinopathy.
- Prolonged Duration of Diabetes The longer you have diabetes, the higher the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy. Over time, chronic hyperglycemia causes damage to retinal blood vessels, increasing the likelihood of vision complications. Even if the regular sugar spikes are under control and you still have a high level of hemoglobin A1C, it will impact your retina.
- High Blood Pressure and Cholesterol High blood pressure and cholesterol levels are directly connected to diabetes. For diabetic patients, high blood pressure and high cholesterol are common, and they can exacerbate the damage to the blood vessels in the retina. Hypertension can even lead to additional stress on these vessels, while high cholesterol can contribute to the formation of fatty deposits in the retina blood vessels, obstructing blood flow.
- Blurred Vision Diabetic retinopathy specialists have seen that as diabetic retinopathy progresses, fluid may leak into the macula, the central part of the retina that gives you a sharp, central vision. The leakage causes swelling, known as macular edema, that causes blurred vision. If you suffer from diabetic retinopathy, you may struggle to focus on fine details, making activities like reading and driving challenging. Diabetic retinopathy can even impair night vision, making it hard to see in low light. This occurs because damaged blood vessels and retinal changes interfere with the retina’s ability to adapt to darkness.
- Floaters or Spots in Vision In advanced stages, bleeding from abnormal retinal blood vessels can cause floaters—small, dark spots or threads that drift across your field of vision. Floaters are caused by bits of blood, cells, or protein in the vitreous gel. A sudden increase in floaters, especially with flashes of light or vision loss, can indicate retinal detachment. Vitrectomy can be the best treatment for diabetic retinopathy in such cases.
- Impaired Color Vision Damage to the retina can affect color perception, as the cones responsible for color vision are disrupted. This can lead to dull or washed-out colors, difficulty distinguishing between shades, and a reduction in color vibrancy, impacting daily tasks.
- Comprehensive Eye Exam The best eye doctor for diabetic retinopathy suggests that a regular comprehensive eye exam is essential for the early detection of eye problems, including diabetic retinopathy. During the exam, diabetic retina specialists will conduct tests to assess your vision and check for signs of retinal damage. These tests may include visual acuity testing to measure how well you see at various distances and tonometry to measure the pressure inside your eyes.
- Dilated Eye Exam In a dilated eye exam, eye drops are used to dilate the pupils, providing a better view of the retina and optic nerve. This allows diabetic retinopathy specialists to inspect the retina more thoroughly for signs of diabetic retinopathy, such as microaneurysms, hemorrhages, and abnormal blood vessel growth.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) OCT is a simple and non-invasive imaging test that involves using light waves to take detailed cross-sectional pictures of the retina. This test helps in identifying areas of retinal swelling, thickness changes, and the presence of macular edema. OCT can detect even subtle changes in the retina, allowing the detection and monitoring of the progress of diabetic retinopathy.
- Fluorescein Angiography Fluorescein angiography involves injecting a fluorescent dye into the bloodstream, which then travels to the blood vessels in the retina. A special camera then takes a series of pictures as the dye passes through the retinal blood vessels. This test highlights any abnormalities in the blood vessels, such as leakage, blockages, or abnormal growth. It provides detailed information about the extent and severity of diabetic retinopathy, guiding options for the best treatment for diabetic retinopathy.
Schedule a Consultation with Best Diabetic Retinopathy Specialists!
Best Treatment for Diabetic Retinopathy
- Blood Sugar Management Maintaining optimal glucose levels is crucial to prevent and slow the progression of diabetic retinopathy. For quick recovery, regularly monitor blood glucose, follow a good and healthy diet, exercise, and take prescribed medications.
- Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Control Controlling blood pressure and cholesterol levels helps reduce additional strain on the retinal blood vessels, preventing the worsening of diabetic retinopathy.
- Medication (e.g., Anti-VEGF Injections) Anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) injections help reduce the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the retina and decrease fluid leakage.
- Laser Photocoagulation
- Laser photocoagulation is effective and the best treatment for diabetic retinopathy, especially during the early stages. During this procedure, a laser is used to precisely target and seal or shrink abnormal blood vessels in the retina. There are two types of laser photocoagulation:
- Focal/Grid Laser Photocoagulation:
This technique is used to treat diabetic macular edema.
- Pan Retinal Photocoagulation (PRP):
This technique is used to treat proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
Laser photocoagulation helps prevent further leakage from damaged blood vessels, thereby reducing the risk of vision loss. Side effects can include temporary blurry vision and loss of peripheral vision, but the benefits of preventing severe vision loss often outweigh these risks.
- Clear blood from the vitreous that obstructs vision.
- Remove scar tissue that can cause traction on the retina, leading to detachment.
- Repair retinal detachment if it is present.
- Treat macular holes or other retinal issues caused by diabetic retinopathy.
- Dexamethasone Implants: The biodegradable implant helps reduce retinal inflammation and fluid accumulation.
- Fluocinolone Acetonide Implants: The non-biodegradable implant provides a sustained anti-inflammatory effect to manage chronic DME.
Why Our Diabetic Retinopathy Specialists are the Best Choice for Your Care?
Diabetic retinopathy specialists at Shri Venkatesh Eye Institute are focused on accurate diagnosis along with the best treatment for diabetic retinopathy. Our eye institute and the surgical center have been serving eye care for more than 40 years with dedicated high-end technologies for patient comfort. From a detailed and comprehensive examination of invasive surgical procedures, we offer the best treatments for diabetic retinopathy and other eye problems.
Shri Venkatesh Eye Institute and Surgical Centre commits to restoring the best vision with core values of Seva, Atithi Devo Bhava, Compassion, Empathy, Sustainability, Harmony, and Arogya for all. Contact us for complete eye care experience with advanced technology. Get treated with care and uncompromised services offered by experts leading the legacy in the eye healthcare sector.
